Ah, curiosity has gotten the best of you, has it? You've heard unfamiliar terms like cryptocurrency, web3, digital IDs, blockchain, etc. Let's take the complexity of the web3 world into simple concepts that we can all understand. So, let's start with the definition of digital ID. Then we'll look at the story of digital IDs, DIDs, how many characters they can have, how digital IDs fit into the cryptocurrency scheme, and your information and data can be yours.
What is digital ID?
A digital ID is a special code that lets computers and other devices know who you are online. It's like a school ID number, a driver's license number, company ID, or social media profile. It's like a digital version of your name, but instead of using letters, it's a bunch of numbers and letters that only computers can understand.
You might use a digital ID when you sign up for an account on a website, a social media site, or an online game. The digital ID helps the website know it's really you when you log in, so you can access your account and do things like post updates, play games, or chat with friends.
Think of it as a secret password to prove your identity to a computer, so you can do things on the internet that only you should be able to do.
The story of digital ID
The concept of digital ID has been around for many years, and it has evolved as technology has advanced and new applications for digital identification have emerged.
One of the earliest examples of digital identification was using passwords and PINs to protect access to computer systems and online accounts. As the internet became more widespread in the 1990s, digital certificates, and secure sockets layer (SSL) technology were developed to enable secure online transactions and communications.
However, in recent years, digital ID has become increasingly important for online security and authentication, and many organizations and governments have developed digital ID systems. For example, some countries have implemented national digital ID programs that enable citizens to access government services and conduct transactions online.
The idea of using digital ID for cryptocurrency and blockchain technology also emerged as these technologies became more popular. The first cryptocurrency, Bitcoin, was created in 2009, and it relied on a unique digital ID system to enable secure transactions and prevent fraud.
Overall, the concept of digital ID has evolved as technology has advanced and new applications for digital identification have emerged. It is now an essential part of many online systems and services, enabling secure authentication and transactions in a digital world.
A specialized ID called a decentralized ID
What's that, you might ask? According to W3C, "Decentralized Identifiers (DIDs) are a new type of identifier that enables verifiable, decentralized digital identity." That's a mouthful, isn't it? Don't worry; I'm going to break it down for you.
Decentralized means spreading data across many computers on a blockchain rather than storing it on one. It makes it harder for hackers to steal data. It's like when students share their work using multiple computers instead of one computer.
How many characters are in a digital ID?
The number of letters and numbers used to identify someone with a digital ID can vary depending on the specific type of ID or system being used.
Some digital IDs, such as a four-digit PIN or a six-character alphanumeric code, may be very short. Others, like your DIDs, may be longer and more complex, such as a 16-digit credit card number or a 32-character password.
The longer it is, the harder it is for someone else to guess or hack into it. But ultimately, the length and complexity of a digital ID will depend on the specific system or service it's being used for.
Where does digital ID fit into the scheme of cryptocurrency?
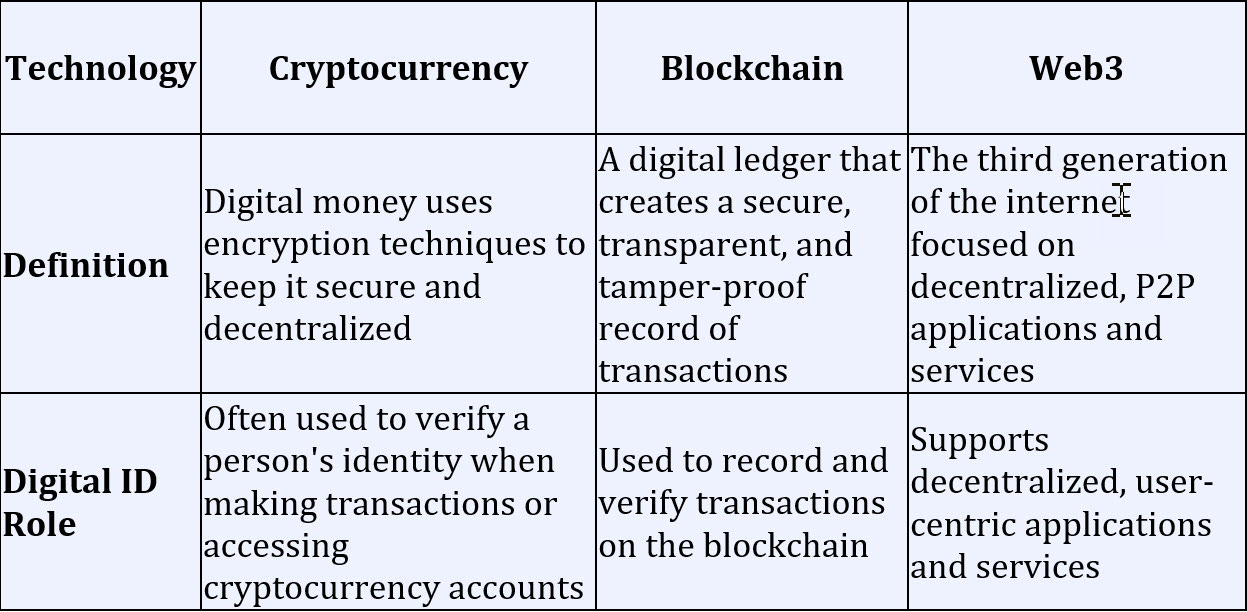
You wouldn't think so, but a digital DID is often used to help verify a person's identity when making transactions or accessing cryptocurrency accounts.
1. Cryptocurrency is a type of digital money that uses encryption (only authorized parties can access it) techniques to keep it secure and to verify and regulate the generation of new currency units. Unlike traditional money, which is subject to regulations by banks and governments, cryptocurrency operates independently and is decentralized.
Instead of physical coins or bills, cryptocurrency is stored in digital wallets protected by special codes called private keys. People can use cryptocurrency to buy goods and services, send money to others, or invest in a currency like a stock.
2. A blockchain is essentially a digital ledger distributed across a computer network. Each block in the chain contains a record of several transactions and a unique code called a hash that identifies the block and links it to the previous block. This creates a secure, transparent, and tamper-proof record of all the transactions on the blockchain.
3. Web3 - Web3, on the other hand, refers to the third generation of the internet, which is focused on decentralized, peer-to-peer applications and services. Cryptocurrency relies on blockchain to record and verifies transactions, while web3 aims to create a more decentralized and user-centric internet.
Your information and data can be yours
Think about a social media platform that is centralized, like Facebook. In this case, all the information and data about your profile and posts are on Facebook's servers, and you have to go through Facebook to connect with your friends and share information. But if the social media platform is decentralized and peer-to-peer, your information and data are on your device, and you can connect and share directly with your friends without going through a central platform.
What more can we say?
So, my frens (that’s short for friends in Web3 talk), did your curiosity take you down the rabbit hole of wanting to know more about cryptocurrency and web3? I know we covered a lot of information. GmNoob is where you want to come for up-to-date and fun information for crypto-curious beginners.
In this session, we talked about digital IDs. We started with what they are. From there, we continued on our journey into the story of digital IDs, DIDs, how many characters they can have, how digital IDs fit into the cryptocurrency scheme, and your information and data can be yours.
Did we answer the questions you may have come up with? Do you have questions that you would like us to cover in our next article? Don’t be bashful; let us know. Oh, by the way, did you know we have podcasts just for beginners?